Unveiling the Power of the 7 Ps of Marketing
Within the realm of marketing, plans are developed, advertising campaigns are started, and goods are sold. However, the 7 Ps of marketing are the foundation of any successful marketing campaign, providing direction and guidance for all marketing decisions and actions.
Originally coined by E. Jerome McCarthy in the 1960s and later popularized by Philip Kotler, the 7 Ps of marketing represent a comprehensive set of variables that marketers can control to influence consumers’ purchasing decisions. From product development to customer engagement, each of the 7 Ps of marketing plays a vital role in shaping the overall marketing strategy of a business. Let’s delve deeper into each of the 7 Ps of marketing and understand its significance in today’s dynamic marketplace.
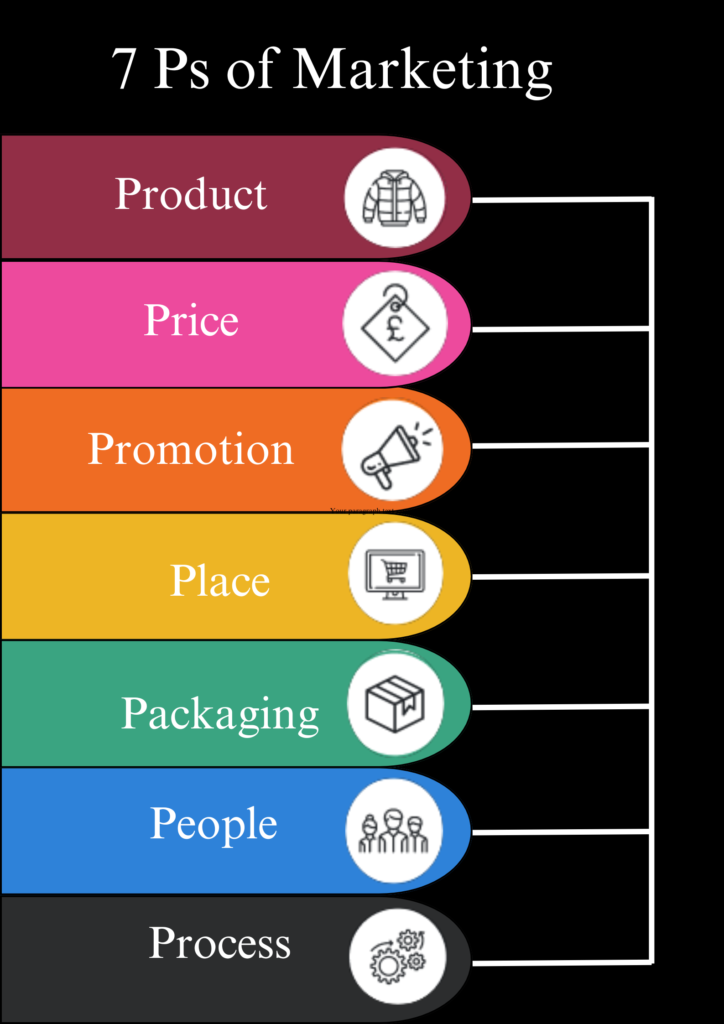
1. Product:
At the heart of any marketing strategy lies the product itself. Whether tangible goods or intangible services, the product is what fulfills the needs and desires of consumers. In today’s hypercompetitive landscape, innovation is key. Marketers must continuously assess market trends, consumer preferences, and technological advancements to develop products that not only meet but exceed customer expectations.
2. Price:
Pricing is a delicate balancing act that directly impacts a company’s bottom line and perceived value. A well-thought-out pricing strategy considers factors such as production costs, competitor pricing, and consumer willingness to pay. From penetration pricing to value-based pricing, marketers must choose a pricing strategy that aligns with their brand positioning and target market.
3. Place:
The distribution channel through which a product reaches its customers is crucial for its success. Whether through traditional retail channels, e-commerce platforms, or direct sales, marketers must ensure that their products are available where and when consumers want them. In today’s digital age, omnichannel strategies that seamlessly integrate online and offline channels have become increasingly important.
4. Promotion:
Promotion encompasses all the communication efforts aimed at persuading consumers to buy a product or service. From advertising and public relations to sales promotions and influencer marketing, the promotional mix is vast and diverse. Marketers must tailor their promotional activities to resonate with their target audience while staying true to their brand identity.
5. People:
People are not only consumers but also employees, stakeholders, and partners who contribute to the success of a business. From frontline staff who interact with customers to executives who shape strategic decisions, every individual plays a role in delivering a positive brand experience. Marketers must invest in employee training, customer service, and relationship management to build strong, lasting connections with their audience.
6. Process:
The processes and systems within an organization can either facilitate or hinder its ability to deliver value to customers. From order processing and inventory management to customer support and feedback mechanisms, streamlined processes are essential for operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Marketers must collaborate with cross-functional teams to identify bottlenecks and implement improvements that enhance the overall customer experience.
7. Physical Evidence:
Tangible cues that reassure customers of the quality and reliability of a product or service fall under the realm of physical evidence. Whether it’s the packaging, store layout, or customer testimonials, these elements shape consumers’ perceptions and influence their purchasing decisions. Marketers must pay attention to every touchpoint along the customer journey and ensure consistency in messaging and branding.
In addition to the traditional 4 Ps—product, price, place, and promotion—McCarthy later introduced the extended marketing mix, which includes people, process, and physical evidence. This expanded framework acknowledges the importance of customer-centricity, operational excellence, and brand credibility in today’s competitive marketplace.
Implementing the 7 Ps of marketing requires a deep understanding of market dynamics, consumer behavior, and industry trends. It’s not enough to simply develop a great product or run a few promotional campaigns. Success lies in the ability to orchestrate all seven elements in harmony, creating a holistic and cohesive marketing strategy that resonates with customers and drives business growth.
In conclusion, the 7 Ps of marketing serve as a timeless roadmap for marketers navigating the ever-evolving landscape of business and commerce. By carefully considering each of the 7 Ps of marketing —product, price, place, promotion, people, process, and physical evidence—marketers can craft compelling strategies that capture the hearts and minds of consumers, ultimately leading to sustained success in the marketplace.
For additional insights, read about how to create a social media calendar that boosts engagement 10X